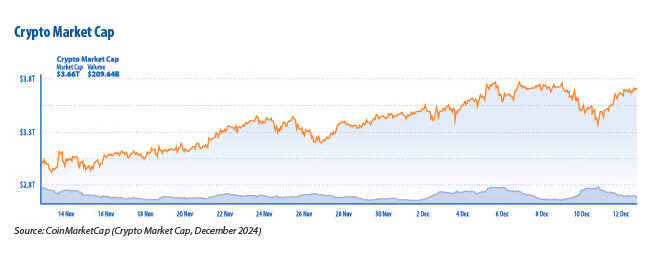
The financial landscape is currently at a pivotal point, as the introduction of Bitcoin in 2009 initiated a significant transformation in digital currency. As of today, the cryptocurrency market stands at a firm $3.66 trillion in total market capitalisation. Research from the Gemini Global State of Crypto Report shows institutional investors pouring capital into digital assets at unprecedented rates, while Bitcoin and Ethereum push toward record valuations in 2024, with the number of users in the cryptocurrency market expected to reach 861 million by 2025.
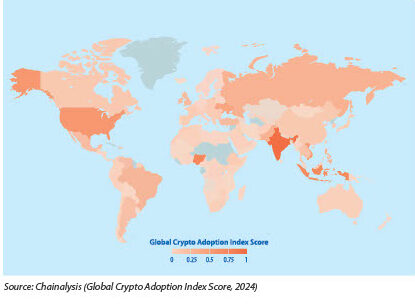
The Bank for International Settlements’ 2024 strategy demonstrates traditional finance’s shifting stance on digital currencies. Their commitment to Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and tokenisation signals a fundamental transformation in how money moves globally. This transformation extends beyond developed economies—Chainalysis’s 2024 Crypto Index highlights countries like Nigeria and India leading cryptocurrency adoption, driven by economic instability and limited banking access.
WHY TRADITIONAL BANKS FEAR THE CRYPTO REVOLUTION
Traditional financial institutions face unprecedented challenges as digital currencies bypass established banking systems. The rise of decentralised f inance threatens long-standing revenue streams while creating new competition for core banking services. Their concerns stem from fundamental changes to how money moves and grows in the digital age.
Bank executives point to three major threats: direct peer-to-peer transactions eliminating profitable intermediary fees, regulatory uncertainty disrupting established compliance frameworks, and growing competition from cryptocurrency investment products offering higher returns. These factors challenge traditional banks’ century-old business models, forcing them to adapt to this new business model.
- The Shifting Power Dynamics Between Centralized and Decentralized Finance
Traditional banking faces unprecedented pressure from Decentralised Finance (DeFi) platforms that operate with remarkable efficiency. DeFi platforms leverage blockchain technology, which ensures transparency and immutability of transactions. This means that every transaction remains visible and verifiable, contrasting sharply with the often opaque operations of traditional banks.
DeFi platforms often offer higher yields compared to traditional f inancial systems. This is because DeFi protocols can operate with lower overhead costs and can offer competitive interest rates to attract users. For example, platforms like Aave and Compound allow users to earn interest on their crypto assets by lending them out to others.
“We’re seeing transaction volumes through crypto networks grow 200% year over year. These aren’t just speculative trades anymore − they’re real economic activity moving outside our system.”
- How Digital Currencies Bypass Conventional Banking Gatekeepers
The impact of digital currencies on traditional banking infrastructure manifests in three key areas:
• Transaction Speed: Cross-border payments now complete in seconds rather than days. A 2022 case study of remittances from the US to Mexico showed how cryptocurrency transfers reduced wait times from 3 to 5 business days to seconds.
• Cost Reduction: Traditional international wire transfers typically cost $35–50. Digital currency transfers often cost $1 or less, regardless of amount or destination. This efficiency particularly benefits small businesses and individuals sending regular cross-border payments.
• Tax Compliance: Digital currencies create automated transaction records, simplifying tax reporting. Financial institutions previously charging premium rates for transaction documentation now face competition from blockchain networks that provide this service inherently.
Venezuelans, for example, use cryptocurrencies to protect their wealth from the country’s challenging 60% inflation rate, while, as of 2023, 16 million Filipinos use cryptocurrency due to a large unbanked population, high smartphone penetration, and reliance on remittances, all of which contribute to widespread adoption.
WALL STREET GIANTS SWITCH SIDES
BlackRock and Fidelity have recently made significant moves into the cryptocurrency space. Both firms launched spot Bitcoin ETFs that saw unprecedented success, each securing almost $4 and $3.5 billion, respectively, in assets within the first month.
This transition is influenced by the growing recognition of Bitcoin as a potential:
1. Hedge Against the Risks of the Financial System
An essential component in the success of these ETFs has been Bitcoin’s rising appeal as a hedge against conventional financial system risks. Investors are seeking substitutes for conventional assets, and Bitcoin’s decentralised nature and limited supply appeal to them. Unlike government-issued currencies, which may be printed at will, Bitcoin’s maximum supply is capped at 21 million coins, generating scarcity and appealing to investors concerned about inflation.
2. “Digital Gold”
Bitcoin is increasingly being recognised as “digital gold” because of its properties as a store of value and a hedge against inflation. Like gold, Bitcoin is considered a possible safe-haven asset, able to guard against the dangers related to conventional f inancial institutions. This view has attracted notable institutional interest in Bitcoin ETFs as well as investment in them.
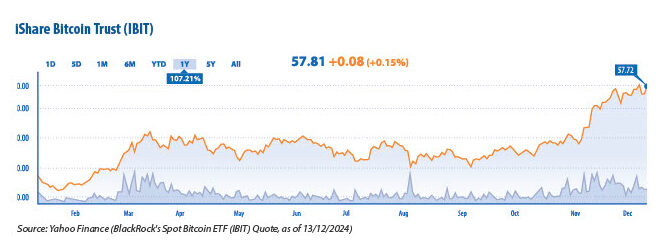
• BlackRock’s Spot Bitcoin ETF (IBIT)
Earlier this year, BlackRock debuted its spot Bitcoin ETF, IBIT. The ETF has now amassed over $10.6 trillion in assets under management (AUM). T his makes it the most successful new ETF in the last four years. IBIT has outperformed all 50+ regional European ETFs combined, some of which have been around for over 20 years. The success of IBIT highlights how institutional investors are rapidly embracing Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies.
Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell
recently compared Bitcoin to gold rather than the US dollar at the DealBook Summit. “People use Bitcoin as a speculative asset. It’s like gold—it’s just virtual and digital,” Powell stated.
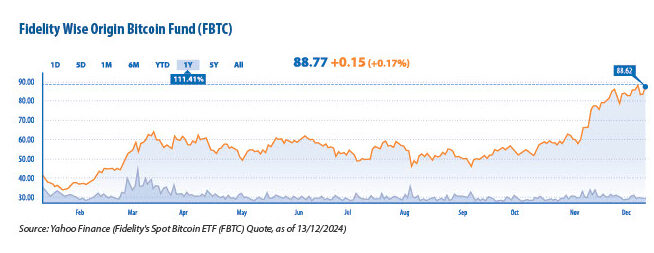
• Fidelity’s Spot Bitcoin ETF (FBTC)
Fidelity also debuted its spot Bitcoin ETF, FBTC, which in its first month of operations had amassed about $3.5 billion in AUM. This rapid buildup is evidence of the significant investor interest in Bitcoin as a vehicle of investment. With the sector having a net inflow of $6.2 billion in November 2024 alone, Fidelity’s ETF has been part of a larger trend of record-high inflows into Bitcoin ETFs.
NATIONS FIGHTING FOR DIGITAL SUPERIORITY
Countries across the globe have varied approaches to regulating and developing cryptocurrency. As China adopts a government-backed digital currency, the United States opts for careful regulation, while the European Union builds structured frameworks. These contrasting strategies reflect each region’s economic priorities and financial management philosophies.
• Why China Banned Bitcoin While Building Its Digital Yuan
Concerns regarding financial risks motivated the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) to enact a cryptocurrency ban in September 2021. This choice reflects larger state control over financial markets and fits the “common prosperity” strategy of the nation. Despite forbidding private cryptocurrencies, China is actively developing its digital yuan (e-CNY or e-yuan). This state-backed digital currency intends to modernise China’s financial system and potentially challenge the US dollar’s supremacy through faster, more affordable payment processing.

• How US Regulators Walk the Tightrope Between Innovation and Control
The US approach balances technological advancement with market stability. President Biden’s March 2022 Executive Order on ensuring Responsible Development of Digital Assets outlined a whole-of-government approach to address the risks and harness the potential benefits of digital assets:
• Consumer Protection: Safeguarding investors against market manipulation and fraud
• Financial Stability: Managing risks to prevent systemic economic disruption
• US Financial Leadership: Maintaining America’s global economic influence
• Financial Inclusion: Expanding access to banking services
• Innovation Support: Fostering technological advancement while maintaining oversight
The administration simultaneously explores CBDC possibilities, considering both opportunities and potential risks to the financial system.
- European Union’s Calculated Approach to Cryptocurrency Adoption
The EU’s Markets in Crypto Assets (MiCA) Regulation represents a structured approach to digital currency integration. This framework prioritises market integrity through clear operational rules, consumer protection via investor safety standards, and f inancial stability by preventing market disruption while promoting growth. The policy also supports innovation by creating space for technological advancement within regulatory bounds.
The EU strategy demonstrates how governments can embrace cryptocurrency benefits while maintaining financial system stability. This balanced approach allows for digital currency innovation without compromising market security or consumer interests. Each region’s distinct strategy reflects differing priorities: China emphasises a state-backed solution, the US balances innovation with regulation, and the EU provides structured integration. These approaches shape how digital currencies will function within global finance.
THE HIDDEN COSTS OF FINANCIAL FREEDOM
The “financial democratisation” through cryptocurrencies presents risks and expenses affecting investors and economies worldwide. Like other transformative financial tools, these digital assets bring significant operational, security, and environmental considerations.
- Why Bitcoin’s Price Swings Keep Central Bankers Awake
Bitcoin’s value fluctuations pose significant concerns for financial regulators. Central banks monitor these price movements closely, as they can affect overall market stability and investor confidence. These rapid value changes occur due to various factors, including regulatory announcements, economic events, and market sentiment shifts.
For example, when China banned cryptocurrency mining, Bitcoin’s value dropped 50% within weeks. Interest rate announcements often trigger immediate price reactions. Largescale trading activities by institutional investors can also cause sudden price movements.
- Tales from the Dark Side of Cryptocurrency Theft and Fraud
The cryptocurrency sector faces ongoing security challenges. Notable cases like the FTX collapse and BitConnect scheme highlight vulnerabilities in digital asset systems. The decentralised structure of cryptocurrencies, while offering freedom from traditional banking systems, creates opportunities for fraudulent activities.
Regulatory bodies work to address these security concerns through:
• Enhanced monitoring systems for suspicious transactions: Coinbase uses the blockchain in partnership with law enforcement to prevent illicit activity in crypto
• Stricter requirements for cryptocurrency exchanges: Mandatory proof of reserves after major platform failures
• Improved investor protection frameworks: the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) mandated disclosure requirements for crypto investment products
• International cooperation on cybercrime prevention: Joint task forces between financial intelligence units worldwide
- The Environmental Price Tag of Mining Digital Gold
Cryptocurrency mining operations leave a considerable environmental footprint. The computational power required for mining consumes substantial energy resources, contributing to increased carbon emissions. Industry participants have begun implementing solutions to address these environmental concerns:
• New ASIC chips drastically reduce power consumption compared to previous generations;
• Mining operations powered by hydroelectric plants in Norway and solar farms in Texas;
• Heat recycling from crypto mining farms for energy for greenhouses;
• Proof-of-stake validation reduces energy usage by 99% compared to proof-of-work.
The environmental impact of cryptocurrency mining has sparked industry-wide discussions about sustainability. While efforts to reduce energy consumption continue, the balance between maintaining network security and environmental responsibility remains a key challenge for the cryptocurrency sector.
These hidden costs demonstrate that financial innovation through cryptocurrencies requires careful consideration of its broader implications for society, the economy, and the environment.
SMALL COUNTRIES PLACE BIG BETS
Smaller countries are leading the way in cryptocurrency adoption, driven more by practical financial needs than speculative interests. These developments provide valuable perspectives on how digital currency can be integrated on a national level.
- El Salvador’s Bitcoin Push
El Salvador’s adoption of Bitcoin as legal tender in September 2021 represented a significant shift in the country’s currency policy. The government distributed $30 worth of Bitcoin to each citizen through Chivo Wallet while installing Bitcoin ATMs nationwide for easy access. Strategic Bitcoin purchases during price dips and plans for a blockchain bondbacked Bitcoin City demonstrate the government’s commitment to this f inancial experiment.
“Anything that can conceive of as a supply chain, blockchain can vastly improve its efficiency —it doesn’t matter if it’s people, numbers, data, money,” former IBM CEO Ginni Rometty rightly pointed out.
- Why Emerging Markets Lead Crypto Adoption Despite the Risks
Countries like India, Nigeria, and Indonesia demonstrate strong cryptocurrency usage patterns, driven by fundamental financial needs. In underserved regions, cryptocurrencies provide essential banking services and reduce international money transfer fees. Argentine workers, for example, convert salaries to stablecoins to guard against peso devaluation.
- Practical Applications in Developing Economies
The Chainalysis 2024 Global Crypto Adoption Index highlights several key uses:
• Local market purchases and bill payments;
• Import-export payments without currency conversion fees;
• Family support payments across borders;
• Guard against local currency inflation.
Local businesses show varying levels of adaptation to the new currency system. Street vendors quickly adopted Bitcoin for small transactions, while retail stores implemented dual pricing systems. Service providers integrated cryptocurrency with existing payment methods, and the tourism sector reported increased interest from crypto-enthusiastic visitors.
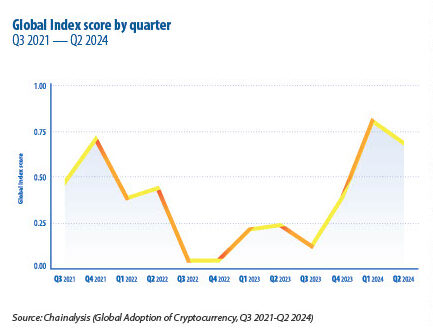
BEYOND THE BITCOIN BUZZ
Cryptocurrency’s impact extends far beyond speculative trading as central banks, supply chains, and legal frameworks adapt to the technology’s expanding influence.
- Why Central Banks Race to Launch Digital Currencies
Central banks worldwide are rapidly developing and piloting CBDCs to modernise financial systems, enhance f inancial inclusion, and maintain economic stability. Here’s how this phenomenon is taking shape all around the globe:
1. The European Central Bank (ECB) is making substantial progress in its efforts to introduce a digital euro. The creation of a Digital Euro Rulebook is the most important aspect of the project. The purpose of this rulebook is to standardise payment procedures throughout the eurozone and to create a consistent user experience. The project intends to improve the payment infrastructure of the eurozone and lessen the region’s reliance on international payment giants such as Visa and Mastercard and other similar organisations.
2. China leads CBDC implementation with its digital yuan (e-CNY or e-yuan) across 26 regions in 17 provinces. The PBOC has been developing the digital yuan since 2014, aiming to elevate the status of the renminbi and challenge the dominance of the US dollar. The digital Yuan offers faster, cheaper, and more secure transactions compared to conventional methods. As of the end of June 2023, the total transaction value of the digital yuan stood at 7 trillion yuan (US$968 billion), which is almost four times the 1.8 trillion yuan noted a year prior, as reported by the PBOC.
3. The G20 and G7 have prioritised digital finance, recognising its potential to foster economic stability and f inancial inclusion. These international forums are working to establish global standards and frameworks for CBDCs to ensure interoperability and security.
The race to launch CBDCs is driven by the need to modernise financial systems, enhance financial inclusion, and maintain economic stability. As central banks continue to develop and pilot these digital currencies, the global financial landscape is set to undergo significant changes.
Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong puts it boldly: “I do think some digital currency will end up being the reserve currency of the world.”
- The Quiet Revolution of Blockchain in Supply Chains
Blockchain technology is transforming supply chains by providing transparency, traceability, and efficiency. Companies such as IBM and Oracle are using blockchain to establish tamper-proof transaction records, which ensure product legitimacy and regulatory compliance. This technology enables organisations to track things from origin to destination, check storage compliance, and streamline payments via smart contracts.
Benefits of Blockchain in Supply Chains:
1. Transparency: Decentralized, immutable ledgers allow stakeholders to verify all transactions;
2. Traceability: Product journeys from origin to destination remain permanently recorded;
3. Efficiency: Smart contracts automate tasks, reducing intermediary needs;
4. Compliance: Tamper-proof records provide reliable audit trails;
5. Fraud Prevention: Real-time visibility enables quick discrepancy detection.
Real-world applications include:
• Food Safety: IBM Food Trust connects farmers, distributors, and retailers;
• Healthcare: Pharmaceutical tracking prevents counterfeit drugs;
• Retail: Authentication systems for luxury goods and diamonds;
• Automotive: Component sourcing and quality standard verification.
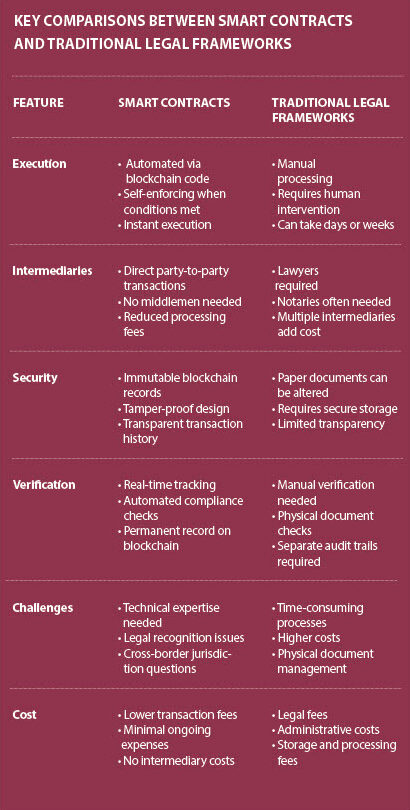
- Smart Contracts vs. Traditional Legal Frameworks
Smart contracts, self-executing agreements with the terms directly written into code, are challenging traditional legal frameworks. They offer automated execution of contractual obligations, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency. However, integrating smart contracts into existing legal systems poses challenges, such as ensuring legal enforceability and addressing jurisdictional issues.
The integration of smart contracts marks a move towards agreement systems that are more automatic and efficient. However, it also brings up important legal and technical issues for future use around the world.
FIVE YEARS FORWARD
Global financial markets watch cryptocurrencies with growing interest as digital assets gain traction beyond speculative trading. Their integration into traditional finance accelerates through institutional investment products and central bank initiatives.
Instead of replacing fiat currency, digital currencies seem to be positioned to complement them. Data shows that they are most popular in emerging economies, where traditional banks fall short. These digital assets excel in cross-border payments, micropayments, and financial inclusion initiatives.
As cryptocurrency hubs grow outside of traditional financial centres, the balance of power in the world’s markets changes. While new payment structures allow programmable and real-time transactions, blockchain technology lessens dependence on existing middlemen.
Still, major challenges still exist. Volatility issues still persist; scalability issues restrict transaction volumes; and unclear regulatory systems exist. CBDCs could offer a formal substitute, therefore influencing the acceptance trends of private cryptocurrencies.
Analytics note that in places where banking options are scarce, cryptocurrencies will expand exponentially. This suggests a time when traditional and digital finance coexist peacefully, therefore promoting more inclusive and effective financial institutions. As these trends quicken, investors should get ready for ongoing change in monetary institutions and payment systems.
By Erfan Alam Serniabat
PHOTO: FEDERAL RESERVE BOARD OF GOVERNORS; PHOTO: ASA MATHAT / FORTUNE LIVE MEDIA / CC BY 2.0

Stay informed anytime! Download the World Economic Journal app on the App Store and Google Play.
https://apps.apple.com/kg/app/world-economic-journal-mag/id6702013422
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.magzter.worldeconomicjournal

