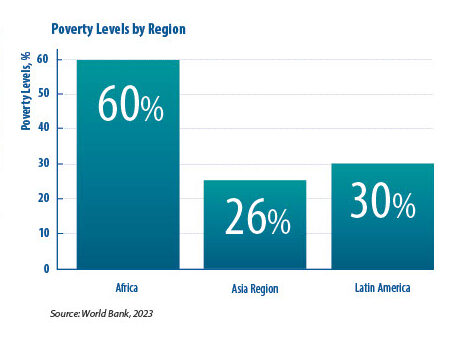
Sustainable development is paramount for developing countries, as it is critical to address challenges such as poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation. According to the World Bank, almost 700 million people are still living in extreme poverty today; most of them live in the Sub-Saharan region of Africa, which alone accounts for 67% of people living in extreme poverty in the world.
On the other hand, global crises such as COVID-19 and the recent commodity crisis have resulted in an increased investment gap from $2.5 trillion to $4 trillion annually. Additionally, with urbanization on the rise, the need for sustainable development is only getting more pressing. By 2050, cities will have to cope with an additional 2.5 billion people. Therefore, sustainable development promises to reduce poverty, guarantee inclusive growth, and build resilient communities that thrive despite climate or economic challenges.
As developing countries grapple with interconnected challenges involving economic growth, social equity, and environmental sustainability, sustainable development continues to be a central vision for many of them. Although progress has been made globally toward meeting the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the results continue to be uneven, especially in developing areas of Africa, Asia, and Latin America. These resource-rich areas are also struggling with the effects of climate change, poverty, inequality, and rapid urbanization.
As urbanization continues, particularly in those areas, providing sustainable infrastructure becomes increasingly challenging. With cities expecting substantial growth, more pressure is placed on resources and public services. This rapid change not only exacerbates environmental issues but also ecosystem degradation.
The global economy is experiencing major, significant change in pursuit of green, comprehensive, and adaptable expansion. Emerging technologies, changes in population, and climatic transformations are all driving this shift, particularly impacting developing regions, which are both profoundly susceptible to such variations yet indispensable to accomplishing sustainable progress worldwide. The World Bank in 2023 observed that worldwide financial gains have become progressively interconnected with eco-friendly methods. For developing countries, though, the goal is to equalize rapid development while guarding the setting and ensuring social well-being. New technologies provide new chances but also create problems in balancing these new opportunities with traditions. Long-established communities struggle to preserve cultural traditions while also adjusting to the changes in the global market.
For many developing regions, the race to modernize and compete globally often leads to environmental and social tensions. Balancing economic development while being eco-friendly remains a key challenge, especially when resources are decreasing. While new technologies offer new opportunities, they should be implemented with consideration for nature and local customs.
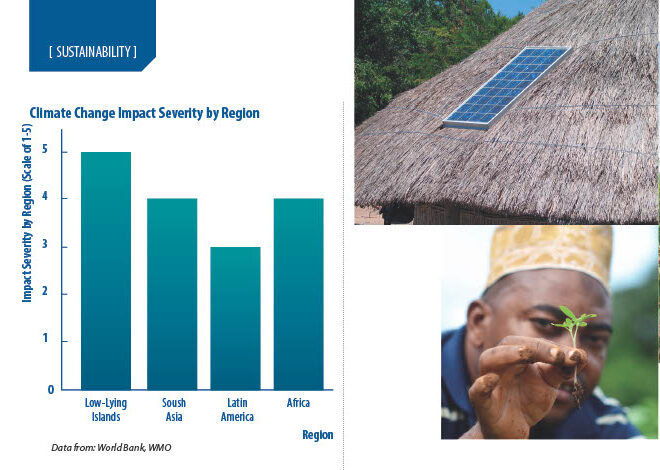
The regions and peoples who inhabit areas prone to the ravages of climate change stand to suffer the most from its effects. Places like low-lying island nations (Pacific, Indian Ocean, and Caribbean islands) and forested areas in the developing world face an uncertain future as temperatures rise and sea levels creep ever higher. Meanwhile, poverty persists in western Yunnan, Southwest China, due to natural and cultural challenges. The area’s rugged terrain and traditions have slowed down development.
“Our biggest challenge in this new century is to take an idea that seems abstract—sustainable development—and turn it into a reality for all the world’s people.” — Ban Ki-moon, Former UN Secretary-General.
Regions, including Africa, Asia, and Latin America, have made progress on these issues, but their improvements have been inconsistent. Africa’s youthful population, Asia’s technological revolution, and Latin America’s green initiatives are central to their sustainability efforts. This report examines the current state of sustainable development in these regions, focusing on progress made up until now and any remaining barriers or challenges left to overcome.
Africa’s youthful population, Asia’s technological revolution, and Latin America’s green initiatives are central to their sustainability efforts
Sustainability Indicators
UNDERSTANDING KEY CHALLENGES IN DEVELOPING NATIONS
Here are some challenges faced by developing countries in relation to SDGs:
• Economic Barriers
Developing countries face important economic barriers in achieving sustainable development, with money being one of the primary issues. According to the IMF, low-income countries often have limited access to capital, making investing in infrastructure, renewable energy, and technology hard.
High poverty rates and youth unemployment remain widespread. In sub-Saharan Africa, over 60% of the population lives on less than $2.15 a day. The rising unemployment rate among youth is particularly alarming, intensifying social instability and obstructing the economic mobility needed for sustainability.
• Social Issues
The UNDP Human Development Report states that inequality in income and opportunity remains pervasive in many developing countries. The wealth gap, particularly between urban and rural populations, continues to limit social mobility and hinder economic progress.
Despite some progress, access to high-quality healthcare and education remains a top priority. In Sub-Saharan Africa and parts of South Asia, fundamental services like primary education and prenatal care are still not widely accessible.
• Environmental Threats
Developing nations are often on the frontlines of environmental destruction and climate change. Climate change threatens many SDGs because of its impacts on ecosystems, biodiversity, and climate-related disasters.
Climate Change Consequences: The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) states that climate events disproportionately affect developing nations, contributing the least to global emissions. North America and Europe experience flooding, landslides, large-scale displacement, and food loss. For example, South Asia is facing erratic weather and rising sea levels.
Loss of Biodiversity: In 2023, the World Bank highlighted that Latin America, the Amazon, and Africa’s Congo Basin are grappling with serious biodiversity reduction, which impacts the economy and the living standards of populations who rely on natural resources.
“In South Asia, maternal health remains a pressing issue. Despite improvements, many women still lack access to essential healthcare services during pregnancy and childbirth.” — Dr. Natalia Kanem, Executive Director of UNFPA.
GEOGRAPHIC NUANCES AND STRATEGIC PERSPECTIVES
As sustainability challenges and opportunities vary widely across the globe, each region offers unique insights into addressing them. From integrating technology to fostering community-driven initiatives, these geographic nuances reveal diverse strategies that contribute to a sustainable future. Let’s explore how different regions are approaching these pressing issues.
• Africa
The sustainability success in Africa depends on a holistic approach that integrates agriculture, natural resource management, and technology simultaneously. In this context, efforts have been made by them increasingly turning to digitalization to overcome the developmental challenges.
Programs for sustainable agriculture and natural resource management:
• The African Development Bank’s Agricultural Transformation Agenda reinforces the drive towards more sustainable agriculture using resilient farming, better water management, and soil health initiatives.
• The Africa Agriculture Development Program (CAADP) is also an initiative aiming to ensure agricultural productivity and progressively improve food security all around the continent. Countries must devote at least 1% of their national budgets to agriculture to ensure a 6% annual growth in the sector. Overall, this program builds not only better agriculture but also enhances land management and water resources and provides rural infrastructure.
• Alliance for a Green Revolution in Africa (AGRA) is another promising project with the goal of facilitating access to higher-quality seeds, fertilizers, and farming techniques. It also advocates for greater agricultural expansion and prone capacity building, market access, and financial inclusion of farmers.
Successes in poverty alleviation through digitalization:
Successes in poverty alleviation using digitalization include Hello Tractor, a platform in Nigeria and other African countries that has significantly increased productivity. According to the company report, farmers with access to the machinery through the platforms observe a 40% increase in productivity. The platform has connected more than 200,000 farmers and allowed them to save time and labor with access to tractor services.
• Asia
While technological innovation and accelerated industrialization have shaped Asia’s development, the continent needs to shift to a green economy today.
Technological innovations for accelerated sustainable development:
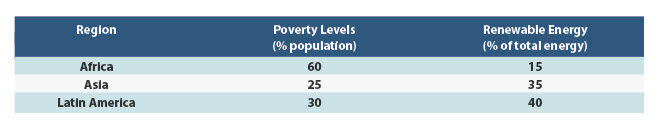
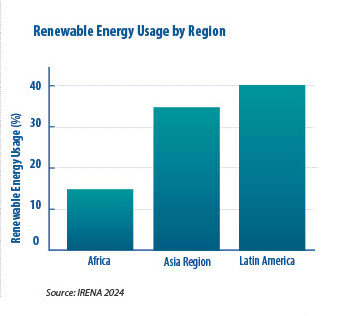
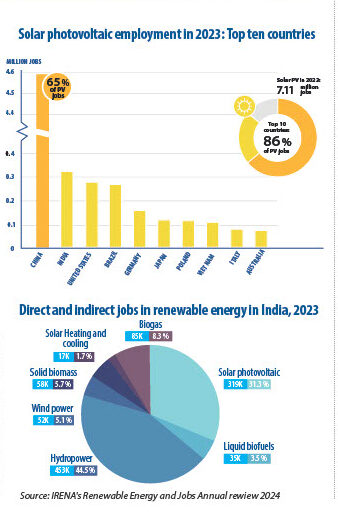
Countries like China and India have carried out renewable energy innovations. India, particularly, has emerged as a world leader in solar power, especially through the National Solar Mission, which plans to install 100 GW of solar energy by 2025. On the other hand, with the Jiuquan Wind Power, China has the largest wind farm on earth, with more than 7,000 turbines and a capacity of 20 GW. T his wind power can supply millions of homes. Plus, it is equipped with an ultra-high-voltage transmission system capable of transferring electric current over very long distances. This particular project continues to expand and is a major step forward for China in renewable energy innovation.
Renewable energy programs and infrastructure development:
Southeast Asia is also making major investments in renewable energy. Countries such as the Philippines and Vietnam are integrating wind, solar, and hydroelectric power into their governmental agendas—a move that, if executed properly, according to the Asian Development Bank (ADB), can help the environment and expand economic opportunities.
According to the International Trade Administration (ITA), ambitious targets have been set in Thailand to increase renewable energy use to over 50% by 2040 through what is called the T hailand National Energy Plan (NEP). The PDP includes major investments in solar, wind, and biomass energy. The government also launched the “Solar Farm” initiative to promote solar energy generation in rural areas.
Singapore has launched the SolarNova program to promote solar energy deployment across the country. It consists of installing solar panels on rooftops of public housing government buildings, targeting 540 megawatts of solar capacity by 2030.
• Latin America
Latin America has been taking the lead with initiatives that include ecology.
Green projects and initiatives in ecology:
The Inter-American Development Bank (IDB) supports efforts towards green energy in the region with projects like Brazil’s Bolsa Verde. It is an initiative rewarding families who adopt sustainable farming practices and environmental conservation measures.
Other projects regarding ecotourism in Costa Rica that preserve biodiversity and uplift local communities highlight Latin America’s progress in using social policies to address poverty and environmental degradation.
PROVEN SUCCESS STORIES
Let’s look at some actual projects with significant impact:
Africa: The “Great Green Wall” Initiative
The Great Green Wall (GGW) is a project that spans 8,000 kilometers from Senegal in the west to Djibouti in the east, covering countries such as Burkina Faso, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Chad, Sudan, and Eritrea.
Objectives
1. Combat desertification
The project aims to stop the spread of the sands from the Sahara by recovering degraded land and encouraging land management practices.
2. Restore biodiversity
The GGW wants to restore ecosystems and enhance biodiversity, which is essential for the survival of the local community.
3.Reduce climate change
By creating forest cover and vegetation, the project wants to contribute to carbon sinks and potentially reduce climate change impact.
4.Develop economy
Create green jobs that benefit locals and improve their lives.
Achievements
As of 2023, the UNCCD reported that this project has restored more than 15 million hectares of land. It has allowed thousands, especially women and youth, to make a living from sustainable agriculture and forestry. Plus, the project has strengthened local engagement and active participation, which encourages communities to take charge of restoring their territories.
Asia: India’s Solar Mission
This program, launched in 2010, is part of the Indian government’s national action plan on climate change. Its primary objective is to ensure India’s transition to green energy sources while reducing reliance on fossil fuels, particularly its overreliance on coal. It targets producing 100 gigawatts (GW) of solar energy by 2025.
Objectives
1. Energy independence
The project aims to reduce India’s reliance on coal by using solar power for electricity as a more reliable energy source.
2. Energy affordability
This initiative helps reduce energy costs for rural communities and improve living standards.
3. Economic opportunities
Create new and diverse jobs from manufacturing and installation to maintenance of solar systems.
4. Technological advancement
Promotes innovative technologies and practices and helps solar energy be efficient and cost-effective.
Achievements
This initiative has helped India achieve a 60 GW solar installation capacity, making it the third-largest solar installation in the world. The country is getting closer to its goal of 100 GW by 2025. According to IRENA, over 1 million jobs have been created thanks to the solar energy sector. This covers areas such as manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and more, without mentioning the important price reduction (down over 80%) since the beginning of the project in 2010. Some rural areas have been equipped with solar home systems, including water pumps and mini-grids.
Latin America: Costa Rica’s Ecotourism
Costa Rica leads in ecotourism. They use their rich biodiversity to build an eco-friendly attraction for tourists. According to the Costa Rican Tourism Institute, ecotourism in the country generates $4 billion each year, accounting for about 8.2% of the nation’s GDP while preserving its forests and wildlife.
Overview
1. Biodiversity and natural resources
The country alone accounts for 5% of the world’s biodiversity. It includes a variety of ecosystems, from rainforests to cloud forests to coastal regions. This diversity makes it a popular destination for nature lovers and eco-tourists.
2. Economic impact
Ecotourism contributes around $4 billion annually to the country’s economy, about 8.2% of the national GDP (ICT). The industry also creates thousands of employment opportunities in hospitality, wildlife conservation, and guided tours.
3. Sustainable practices
This approach to promoting tourism activity with minimal environmental impact encourages green hotels, eco-friendly transport, and wildlife conservation initiatives.
4. Community involvement
Local communities are actively involved and provided with economic opportunities. Community-based tourism helps ensure that at least some tourism revenue goes to residents, creating a sense of ownership over natural resources.
REGIONAL SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT INITIATIVES TABLE
The regional sustainable development initiatives table compares sustainability efforts across regions. It outlines key initiatives, challenges, and outcomes for Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, Latin America, and Asia, showcasing how they address climate change, urbanization, and biodiversity through targeted strategies.
Role of international organizations (UN, World Bank, UNCTAD) in supporting sustainable development International organizations like the UN, World Bank, and UNCTAD play an important role in supporting sustainable development projects globally. Regarding their roles in the projects mentioned previously, here is what to consider:
• The Great Wall Initiatives
UNCCD: Help African countries to work together, providing resources and coordination of land restoration projects. World Bank: Provide loans for sustainable land management and green jobs.
UNDP/UNEP: Provide technical knowledge and collaborate with communities to ensure that the restoration is delivering and restoring species.

• India’s Solar Mission
Asia World Bank: Provide financial and technical assistance to expand solar energy in the country.
UNFCCC/GCF: Facilitate the policy alignment with international climate agreements.
IRENA: Offers guidance on renewable energy technologies and helps create jobs in the solar sector.
• Costa Rica’s ecotourism
UNWTO: Promote Costa Rica’s ecotourism around the world, bring visitors, and build infrastructure.
World Bank: Provide funding for environmental conservation and sustainable tourism development.
UNEP: Ensures eco-friendly tourism practices and supports sustainable tourism policies. Therefore, these institutions are crucial in helping nations realize sustainable development through resource delivery, technical support, and global collaboration.
International organizations like the UN, World Bank, and UNCTAD play an important role in supporting sustainable development projects globally

PROSPECTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
As we look toward 2025, developing regions such as Africa, Asia, and Latin America are expected to experience significant transformations in terms of sustainable investments. Here’s a look at projected trends and developments from region to region:
• Africa
1. Growing need for sustainable investment
Urbanization and climate change are likely to worsen challenges related to food security, water scarcity, and infrastructure gaps. T he following agricultural and technological practices should be prioritized:
- Resilient Farming Techniques: a. Adoption of drought-resistant crop varieties to reduce the effects of climate change. b. Implementation of agroforestry systems that integrate trees into farming landscapes to improve soil fertility and biodiversity.
- Precision Agriculture: a. Use of GPS technology and data analytics to improve planting, watering, and harvesting, reducing resource waste. b. Deployment of remote sensing technologies to monitor crop health and predict pest outbreaks.
- Sustainable Water Management: a. Increasing the use of drip irrigation to save water in dry areas. b. Development of rainwater harvesting systems to support small farmers.
- Capacity Building and Education: a.Training programs for farmers to learn modern techniques and financial skills. b. Partnerships with local universities and NGOs to provide tools and share knowledge.
2. Digitalization
As digitalization continues, it will play a big role in fostering economic development. Technological innovations may bring economic opportunities, particularly in fintech, e-commerce, telemedicine, and other sectors. Strengthening digital infrastructure will improve service delivery in education, health, and public services, filling the equity gap in access and quality.
3. Renewable energy expansion
Africa is likely to see significant investment in renewable energy projects, particularly solar and wind because of its various existing projects. This transition will increase accessibility to energy sources in rural communities while decreasing fossil fuel consumption.
• Asia
1. Technological innovation
Asia is expected to continue to lead the world in technology innovation. Countries like China, India, and Japan are likely to be the top in the sector.
Innovation is essential if we are to transition to a low-carbon economy. Inventions such as energy storage technologies, smart grids, and electric cars are key to making that happen. Here is how they can contribute:
Solar Energy: Initiatives like India’s National Solar Mission generating 100 GW of solar energy will help reduce dependency on coal and other fossil fuels.
Wind Power: China’s Jiuquan Wind Power Base, delivering 20 GW of clean energy will support the country’s growing urban energy needs.
2. Green energy focus
Investing in green technology means focusing on sustainable agriculture and water management. At the same time, it poses great opportunities for man to create a better environment while promoting economic growth.
Governments and companies are expected to work more in synergy on initiatives that save the environment and cut carbon emissions like the use of lithium-ion batteries and green hydrogen to store energy.
3. Urbanization challenges
Urbanization will continue to grow rapidly, accompanied by rising pollution and heavier demand for infrastructure. Governments should concentrate on developing smart cities with renewable energy integration, such as solar rooftops, and wind-powered grids to meet the demands of growing urban populations. They should also reduce pollution levels in cities like Beijing and Delhi through the adoption of large-scale electric vehicles.
India’s National Solar Mission generating 100 GW of solar energy will help reduce dependency on coal and other fossil fuels
• Latin America
1. Social welfare programs
The expansion of social welfare in Latin America is expected to increase. Sustainable agriculture and environmental protection are two areas that will receive much attention when it comes to programs that are both social and environmental.
2. Environmental sustainability
Countries in the region will pay more attention to the conservation of biological diversity and the natural endowment in addition to the adoption of sustainable agriculture and forestry strategies. Funding for renewable energy sources like wind and solar will increase as key strategic objectives to reduce reliance on greenhouse gases.
3. Public-private partnerships
Collaborative efforts between governments, NGOs, and the private sector will increase as they are essential for funding and implementing sustainable development initiatives.

Practical steps for advancing green energy and social reforms in the region:
• Develop Financial Inclusion Programs
Create microfinance programs to support small businesses and farmers in adopting eco-friendly technologies. Provide low-interest loans for households to install renewable energy systems or adopt sustainable practices.
• Improve Education and Skills Training
Establish green job training centers focusing on skills for renewable energy industries, such as solar panel installation and maintenance. Collaborate with universities and NGOs to provide scholarships for environmental science and renewable energy studies
• Strengthen Land and Resource Rights
Launch fair land redistribution programs to help small farmers adopt sustainable practices. Protect Indigenous land rights to ensure their involvement in biodiversity conservation.
BEST STRATEGIES FOR SUSTAINABLE GROWTH
Adopting comprehensive and forward-thinking strategies is essential to achieving long-term sustainability while balancing economic, environmental, and social goals.
1. Governments must prioritize funding for clean energy (solar, wind, and biomass), sustainable agriculture practices, and green technologies (EVs, carbon capture systems).
2. Governments and private companies should collaborate to expand projects in infrastructure and renewable energy. Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) facilitate the mobilization of financial resources, spur innovation, and ensure efficient implementation.
3. Education and skills in green industries should be promoted. That way, countries will have a workforce capable of ensuring long-term sustainability.
4. Cities should adopt eco-friendly designs, architecture, and smart transportation to reduce environmental impact and enhance urban livability.
5. The government should establish policies rewarding sustainable actions as incentives. This includes but is not limited to taxing carbon, offering rebates for green innovations, ensuring regulation of waste emissions and environmental waste, and subsidizing research to build clean energy sources.
CONCLUDING PERSPECTIVES
Sustainable development is crucial for developing countries to tackle poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation. While progress has been made in Africa, Asia, and Latin America, disparities persist. Each region presents unique challenges and opportunities; Africa’s focus on digitalization and sustainable agriculture, Asia’s leadership in renewable energy technologies, and Latin America’s balancing ecosystem protection and social equality.
Overcoming these challenges requires a unified global effort. A comprehensive approach is needed to build resilient economies. This includes increased renewable energy investment, infrastructure development, and public-private partnerships. Regional cooperation should be complemented by strong international support to address resource gaps and ensure fair progress. As stated by Kofi Annan, former UN Secretary-General :”Recognizing that sustainable development, democracy, and peace are indivisible is an idea whose time has come.” Sustainable development requires combining these principles to create a world where economic growth, environmental protection, and social fairness thrive in harmony.
By Naitana Jn Baptiste
PHOTO: PXHERE.COM; PHOTO: IMF PHOTO / TAMARA MERINO / CC BY-NC-ND 2.0; PHOTO: WANG AN QI / SHUTTERSTOCK; PHOTO: D THOMPSON / CHATHAM HOUSE / CC BY 2.0; HOTO: LUKELAKE79 / SHUTTERSTOCK; GLOBALBOOKENDS / CC BY-SA 4.0; PHOTO: NAYPONG STUDIO / ADOBE STOCK; MWANZO MILLINGA / UNCTAD / CC BY-SA 2.0; PHOTO: WIRESTOCK CREATORS, ECOPRINT / SHUTTERSTOCK; HOTO: CHRISTIAN HESS ARAYA / UNSPLASH; HOTO: IMF PHOTO / TAMARA MERINO / CC BY-NC-ND 2.0; PHPTO: DEWALD KIRSTEN / SHUTTERSTOCK;
Stay informed anytime! Download the World Economic Journal app on the App Store and Google Play.
https://apps.apple.com/kg/app/world-economic-journal-mag/id6702013422
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.magzter.worldeconomicjournal

